CMIP6 Data
HISTORICAL GREENHOUSE GAS CONCENTRATIONS FOR CMIP6
Meinshausen, M., Vogel, E., Nauels, A., Lorbacher, K., Meinshausen, N., Etheridge, D. M., Fraser, P. J., Montzka, S. A., Rayner, P. J., Trudinger, C. M., Krummel, P. B., Beyerle, U., Canadell, J. G., Daniel, J. S., Enting, I. G., Law, R. M., Lunder, C. R., O'Doherty, S., Prinn, R. G., Reimann, S., Rubino, M., Velders, G. J. M., Vollmer, M. K., Wang, R. H. J., and Weiss, R.: Historical greenhouse gas concentrations for climate modelling (CMIP6), Geosci. Model Dev., 10, 2057-2116, 2017.
Available online resources:
- The manuscript
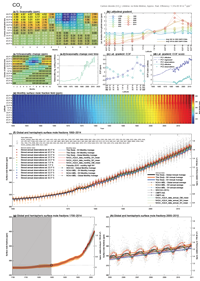
- The supplement with additional figures and annual-mean data (37 MB)
- The GHG Factsheets and data download links
HISTORICAL GREENHOUSE GAS CONCENTRATIONS FOR CMIP6
---------------------------------------------------------------------
CMIP6 INPUT FILES
OF GHG CONCENTRATIONS
FOR CONCENTRATION DRIVEN
HISTORICAL RUNS
FROM 1850 to 2014
---------------------------------------------------------------------
VERSION:
This is final data.
Data VERSION:
1 July 2016. (same as in final manuscript release on 31 May 2017)
NAME OF DATA SET:
Historical CMIP6 GHG CONCENTRATIONS.
COVERAGE:
Surface mole fractions of the big three greenhouse gases, namely
- CO2,
- CH4,
- N2O,
as well as 17 ozone depleting substances, namely:
- CFC-12,
- CFC-11,
- CFC-113,
- CFC-114,
- CFC-115,
- HCFC-22,
- HCFC-141b,
- HCFC-142b,
- CH3CCl3,
- CCl4,
- CH3Cl,
- CH2Cl2,
- CHCl3,
- CH3Br,
- Halon-1211,
- Halon-1301,
- Halon-2402,
and 23 other fluorinated compounds, namely,
- HFC-134a,
- HFC-23,
- HFC-32,
- HFC-125,
- HFC-143a,
- HFC-152a,
- HFC-227ea,
- HFC-236fa,
- HFC-245fa,
- HFC-365mfc,
- HFC-43-10mee,
- NF3,
- SF6,
- SO2F2,
- CF4,
- C2F6,
- C3F8,
- C4F10,
- C5F12,
- C6F14,
- C7F16,
- C8F18,
- c-C4F8,
In addition to these individual species, there are three equivalence species
- CFC-12-eq, which is a radiative-efficiency-weighted sum of all ODS: 'CFC-12', 'CFC-11', 'CFC-113', ...
'CFC-114', 'CFC-115', 'HCFC-22', 'HCFC-141b', 'HCFC-142b',...
'CH3CCl3', ...
'CCl4', 'CH3Cl', 'CH2Cl2', 'CHCl3', 'CH3Br', 'Halon-1211', ...
'Halon-1301', 'Halon-2402' - HFC-134a-e, which is a radiative-efficiency-weighted sum of all GHGs, except CO2, CH4, N2O and gases summarized by CFC-12-eq: 'HFC-134a', 'HFC-23', ...
'HFC-32', 'HFC-125', 'HFC-143a', 'HFC-152a', 'HFC-227ea', ...
'HFC-236fa', 'HFC-245fa', 'HFC-365mfc', 'HFC-43-10mee', ...
'NF3', 'SF6', 'SO2F2', 'CF4', 'C2F6', 'C3F8' ...
'C4F10' 'C5F12' 'C6F14' 'C7F16' 'C8F18' 'c-C4F8' - CFC-11-eq, which is a radiative-efficiency weighted sum of all GHGs, except CO2, CH4, N2O and CFC-12: 'HFC-134a', 'HFC-23', ...
'HFC-32', 'HFC-125', 'HFC-143a', 'HFC-152a', 'HFC-227ea', ...
'HFC-236fa', 'HFC-245fa', 'HFC-365mfc', 'HFC-43-10mee', ...
'NF3', 'SF6', 'SO2F2', 'CF4', 'C2F6', 'C3F8' ...
'C4F10' 'C5F12' 'C6F14' 'C7F16' 'C8F18' 'c-C4F8' ...
'CFC-11', 'CFC-113', ...
'CFC-114', 'CFC-115', 'HCFC-22', 'HCFC-141b', 'HCFC-142b',...
'CH3CCl3', ...
'CCl4', 'CH3Cl', 'CH2Cl2', 'CHCl3', 'CH3Br', 'Halon-1211', ...
'Halon-1301', 'Halon-2402'
See the draft manuscript for further explanation of how to use those gases, potential vertical extensions etc.
CONTRIBUTORS:
Malte Meinshausen1,2,3 Elisabeth Vogel1,2, Alexander Nauels1,2, Katja Lorbacher1,2, Nicolai Meinshausen4, David Etheridge5, Paul Fraser5, Stephen A. Montzka6, Peter Rayner2, Cathy Trudinger5, Paul Krummel5, Urs Beyerle7, Josep G. Canadell8, John S. Daniel9, Ian Enting10, Rachel M. Law5, Simon O’Doherty11, Ron G. Prinn12, Stefan Reimann13, Mauro Rubino5,14, Guus J.M. Velders15, Martin K. Vollmer13, Ray Weiss16
Affiliations:
(1) Australian-German Climate & Energy College, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, Australia
(2) Department of Earth Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, Australia
(3) Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Potsdam, Germany
(4) Seminar for Statistics, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich), Zurich, Switzerland.
(5) CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Aspendale, Victoria, Australia
(6) NOAA, Earth System Research Laboratory, Global Monitoring Division, Boulder, Colorado, USA
(7) Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich (ETH Zurich), Switzerland
(8) Global Carbon Project, CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Canberra, ACT, Australia
(9) NOAA, Earth System Research Laboratory, Chemical Sciences Division, Boulder, Colorado, USA
(10) The University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia (retired)
(11) University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom
(12) MIT, Cambridge, MA, United States
(13) Empa, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology, Laboratory for Air Pollution and Environmental Technology, Switzerland
(14) Dipartimento di matematica e fisica, Seconda Università degli studi di Napoli, 81100 Caserta, Italy
(15) National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM), Bilthoven, Netherlands
(16) Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, CA, United States
REFERENCE:
When using the data, please cite:
Meinshausen, M., Vogel, E., Nauels, A., Lorbacher, K., Meinshausen, N., Etheridge, D. M., Fraser, P. J., Montzka, S. A., Rayner, P. J., Trudinger, C. M., Krummel, P. B., Beyerle, U., Canadell, J. G., Daniel, J. S., Enting, I. G., Law, R. M., Lunder, C. R., O'Doherty, S., Prinn, R. G., Reimann, S., Rubino, M., Velders, G. J. M., Vollmer, M. K., Wang, R. H. J., and Weiss, R.: Historical greenhouse gas concentrations for climate modelling (CMIP6), Geosci. Model Dev., 10, 2057-2116, 2017.
Manuscript (available here) is part of the CMIP6 Special Issue, Geoscientific Model Developoment, edited by Eyring et al., March 2016.
SPACE AND TIME RESOLUTION:
File 1*: Global with latitudinal 0.5 degree bins and monthly resolution (filename-code: '_gr2-0p5x360deg_000001-201412')
File 2: Global with latitudinal 15 degree bins and monthly resolution (filename-code '_gr-15x360deg_000001-201412')
File 3: Global and hemispheric means with monthly resolution (filename-code '_gr3-GMNHSH_000001-201412')
File 4: Global and hemispheric means with annual resolution (filename-code '_gr3-GMNHSH_0000-2014')
* Note that this fine latitudinal resolution is not the resolution of the underlying spatial information and only provided as a smooth, yet mean-preserving interpolation of the 15-degree latitudinal files to assist modelling groups in implementing the 15-degree files in their atmospheric grids.
DATA FORMAT:
The data is made available netcdf, CSV (files 2-4), XLS, and Matlab .mat (R2016a) files.The datapoints are given as area-averages for the centre of each equal-latitude bin, hemisphere or the global domain. The monthly values are given as time-averages for that respective month or year.
RECOMMENDED USE:
If possible, please prescribe the (gridded) surface concentration fields
with monthly and latitudinal resolution for the concentration-driven
historical CMIP6 runs. Alternatively, modelling groups can choose to only presribe hemispheric
or even global means. Note however, that a bias of too little forcing
in the Northern hemisphere might be introduced, if globally uniform
concentrations of CO2 and CH4 were assumed. Please document clearly your choice.
The provided datasets are surface concentrations. it is assumed that
modelling groups have their own capabilities to propagate those concentrations
vertically throughout the troposphere and stratosphere. Options for a default vertical extension are provided in the Meinshauen et al. manuscript., GMD
KNOWN ISSUES:
- 26 July 2016: The annual netcdf files’ time axis is offset by one year. That error seems to be affecting all mole_fraction_of_XXX_in_air_input4MIPs_GHGConcentrations_CMIP_UoM-CMIP-1-1-0_gr3-GMNHSH_0000-2014.nc files. The time axis in corresponding csv, mat and xls files seems to be correct (same name, ending with .csv, .mat and .xlsx, respectively). The correct annual data time axis starts in year 0 and ends in year 2014 (not 2015). Thanks to Olivier Boucher for spotting that.
PERIOD OF RECORD:
Data available from 0 (1 BC) to Year 2014, inclusive.
The period to be used for the historical CMIP6 run is 1850 to 2014.
THANKFUL ACKNOLWEDGEMENT:
This data is composed from a large number of station data and
icecore records. The contributions the respective measurement initiatives
and data compilers (especially NOAA ESRL and AGAGE networks) did, is
greatfully acknowledged and this product would not have been
possible without those vital datasets. The full list of references
is going be included in time for the final data release.
CONTACT:
Please contact Malte Meinshausen, Climate & Energy College,
The University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
malte.meinshausen@unimelb.edu.au
with any suggestions or bug reports in regard to the data, format, or description.
Please feel free to do so by phone (Australian time): +61 390356760
Thank you.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
DOWNLOAD:
Either via the search function (look for Institution being "UoM" - which stands for University of Melbourne) here:
https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/search/input4mips/
download data directly via our colleague's FTP server at ETH Zurich (Thanks to Urs Beyerle).
ftp://data.iac.ethz.ch/CMIP6/input4MIPs/UoM/GHGConc/CMIP
or get download links for specific files here:
http://climate-energy-college.org/ghg-factsheets
---------------------------------------------------------------------
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 9.34 MB | |
| 15.33 MB |